What ligands bind to integrin?
Integrin-Ligand specificity
Humans have at least 18 α subtypes and 8 β subtypes which together generate 24 known binding pairs for the integrins heterodimer (reviewed in [1][2]). The α subunit of the integrin heterodimer especially the αI domain determines the ligand specificity for cell-ECM adhesion (reviewed in [3]). The characteristic of integrin subunits is their ability to bind diverse matrix molecules imparted by the heterogeneity of the monomers; this plasticity is instrumental for cell-ECM binding and subsequent mechanotransduction events.
The amino acid sequence: arginine-glycine-aspartic acid, or RGD motif, is commonly accepted as a general integrin-binding motif on target ligands, however, individual integrins can also recognize other protein-specific motifs (reviewed in [1][2][3]).
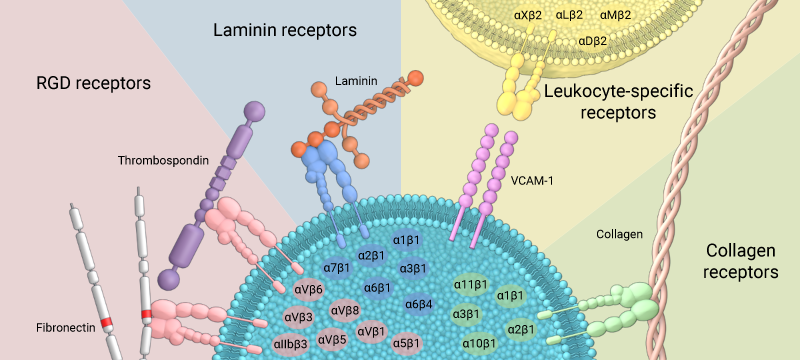
Integrins can bind to a diverse range of ligands, which can be broadly categorised into: RGD receptors, laminin receptors, leukocyte-specific receptors, and collagen receptors.
Common ECM components that are bound by integrins (with respective recognition sequence) are:
- Fibronectin (RGD, LDV)
- Collagen(triple helical GFOGER)
- Laminin (RGD)
- Fibrinogen(RGD)
- Thrombospondin
- Glycoproteins (e.g. tenascin C , osteopontin, nefronectin)
Immunologically important integrin ligands are the inter-cellular adhesion molecules (ICAMs), immunoglobulin superfamily members present on inflamed endothelium and antigen-presenting cells.
Integrins are broadly grouped into four categories based on their ligand-specificity (reviewed in [2]):
- RGD receptors (α5β1, αVβ3, αVβ1,αVβ5, αVβ6, αVβ8, and αIIbβ3)
- Laminin receptors (α1β1, α2β1, α3β1, α6β1, α7β1, and α6β4)
- Leukocyte-specific receptors (αLβ2, αMβ2, αXβ2, and αDβ2)
- Collagen receptors (α1β1, α2β1, α3β1, α10β1, and α11β1)
References
- Barczyk M, Carracedo S, and Gullberg D. Integrins. Cell Tissue Res. 2009; 339(1):269-80. [PMID: 19693543]
- Takada Y, Ye X, and Simon S. The integrins. Genome Biol. 2007; 8(5):215. [PMID: 17543136]
- Humphries JD, Byron A, and Humphries MJ. Integrin ligands at a glance. J. Cell. Sci. 2006; 119(Pt 19):3901-3. [PMID: 16988024]


