What is Arf6-associated endocytosis?
Arf6-associated endocytosis is a clathrin-independent, plasma membrane-endosomal recycling pathway, regulated by the Arf6 protein, which is a member of the Arf family of small GTPases [1]. In this pathway, Arf6 cycles between the inactive GDP-bound state and active GTP-bound state. At the plasma membrane Arf6-GTP facilitates internalization of various cargos using energy from GTP hydrolysis, following which, the inactive Arf6-GDP associates with the tubular recycling endosome. Upon further activation by guanine nucleotide exchange factors like Grp1-associated scaffold protein (GRASP) [2], Arf6-GTP relocates to the plasma membrane and forms protrusive actin-rich structures, recycling membrane back to the cell surface. The Arf6-associated endocytic route requires cholesterol and correspondingly, the Arf6-associated endosomes are rich in cholesterol and PIP2 [3].
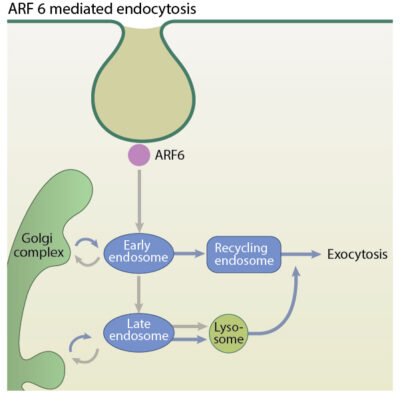
A clathrin independent pathway dependent on the active GTP-bound or inactive GDP-bound state of Arf6 protein
Glycosyl phosphatidylinositol anchor proteins (GPI-APs) like CD55 and CD59, proteins involved in immune function such as MHC Class 1, CD1a, and cell adhesion proteins like cadherins and integrins are some examples of cargo internalized and recycled by this pathway. In fact, Arf6-associated endocytosis is emerging as an important trafficking pathway that regulates cell adhesion, migration, tumor invasion and cytokinesis (reviewed in [4]). NEDD9, a marker as well as therapeutic target for metastatic breast cancer, inactivates Arf6, blocking the recycling of matrix metalloproteinase 14 (MMP14) back to the cell surface, thus increasing MMP14 activity and facilitating tumor invasion [5].
References
- Radhakrishna H, and Donaldson JG. ADP-ribosylation factor 6 regulates a novel plasma membrane recycling pathway. J. Cell Biol. 1997; 139(1):49-61. [PMID: 9314528]
- Venkataraman A, Nevrivy DJ, Filtz TM, and Leid M. Grp1-associated scaffold protein (GRASP) is a regulator of the ADP ribosylation factor 6 (Arf6)-dependent membrane trafficking pathway. Cell Biol. Int. 2012; 36(12):1115-28. [PMID: 22931251]
- Naslavsky N, Weigert R, and Donaldson JG. Characterization of a nonclathrin endocytic pathway: membrane cargo and lipid requirements. Mol. Biol. Cell 2004; 15(8):3542-52. [PMID: 15146059]
- Schweitzer JK, Sedgwick AE, and D’Souza-Schorey C. ARF6-mediated endocytic recycling impacts cell movement, cell division and lipid homeostasis. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2010; 22(1):39-47. [PMID: 20837153]
- Loskutov YV, Kozyulina PY, Kozyreva VK, Ice RJ, Jones BC, Roston TJ, Smolkin MB, Ivanov AV, Wysolmerski RB, and Pugacheva EN. NEDD9/Arf6-dependent endocytic trafficking of matrix metalloproteinase 14: a novel mechanism for blocking mesenchymal cell invasion and metastasis of breast cancer. Oncogene 2014; 34(28):3662-75. [PMID: 25241893]


