What are transcription factories?
The primary role of chromatin assembly is the compaction of an otherwise very long DNA molecule into discrete structures that fit into the nucleus. However, this compaction cannot be achieved at the expense of a cells ability to transcribe and replicate DNA. Recent findings have highlighted several properties intrinsic to the assembly and arrangement of chromosomes that retain access to genomic DNA and contribute to the regulation of gene expression.
Despite 20,000 genes being present in each haploid nucleus, the number of transcription foci is limited to around 2000. These transcription foci, also known as transcriptional factories are distinct submicron nuclear regions that are associated with nascent RNA production and are enriched in RNA polymerase II (RNA pol II) complexes [1]. The limitation in the ratio of transcriptional foci per genes to be transcribed is overcome by a phenomenon where groups of genes share the same transcription machinery. These genes are considered to be co-transcribed. Co-transcribed genes are, however, arranged on a linear DNA molecule, and not necessarily adjacent to each other. In order for these distant genes to be transcribed by the same transcription factory, they must first co-localize with this machinery. Indeed, various dynamic properties, and molecular processes, have been identified that promote this very phenomenon. For example, chromosome dynamics and the spatial distribution of genes may lead to the active redistribution of genes and chromosomal regions. In other cases, post translational modification of the chromatin, or active remodeling of chromatin by ATP powered proteins, facilitates this process.
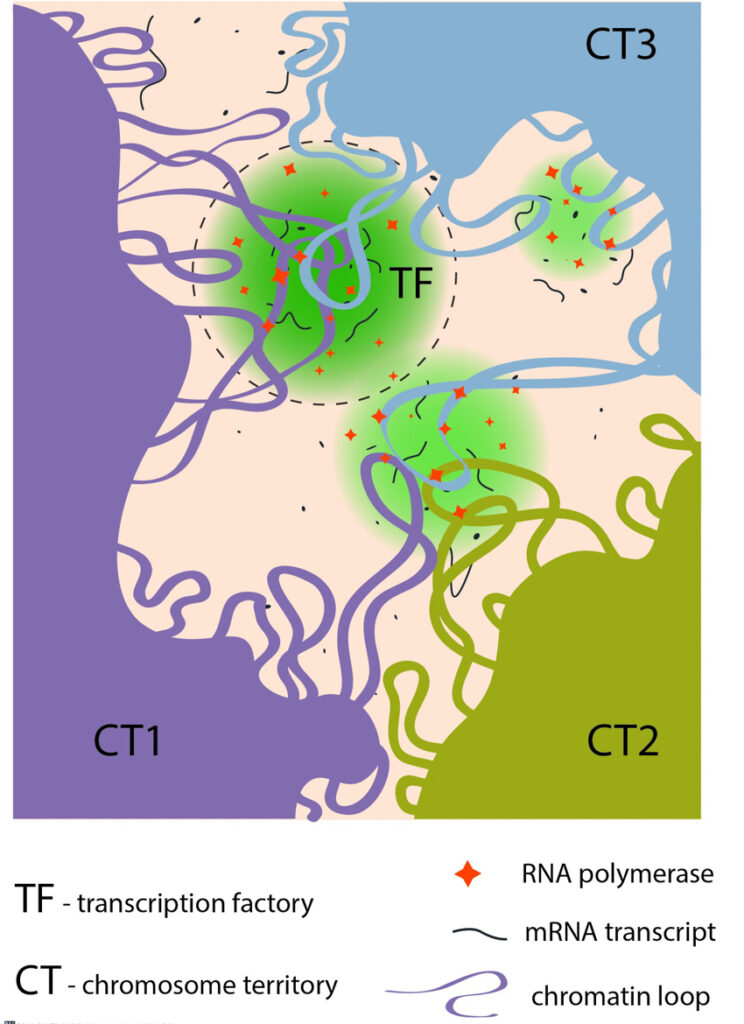
Chromatin loops from the same or from different chromosome territories often share transcription factories (TFs). TFs are enriched in RNA polymerase II complexes that produce nascent RNA transcripts, using co-transcribed genes from chromatin loops as their templates.


